
As home prices continue to soar, the dream of homeownership feels increasingly out of reach for many Americans. With decades of underbuilding leading to a massive housing shortage, families are finding it harder than ever to secure a place to call home. But what if there was a solution that could make building homes faster, more affordable, and more efficient? Enter modular homes—a construction method making a strong comeback and offering hope for a new, more accessible path to homeownership.
A Blast from the Past with a Modern Twist
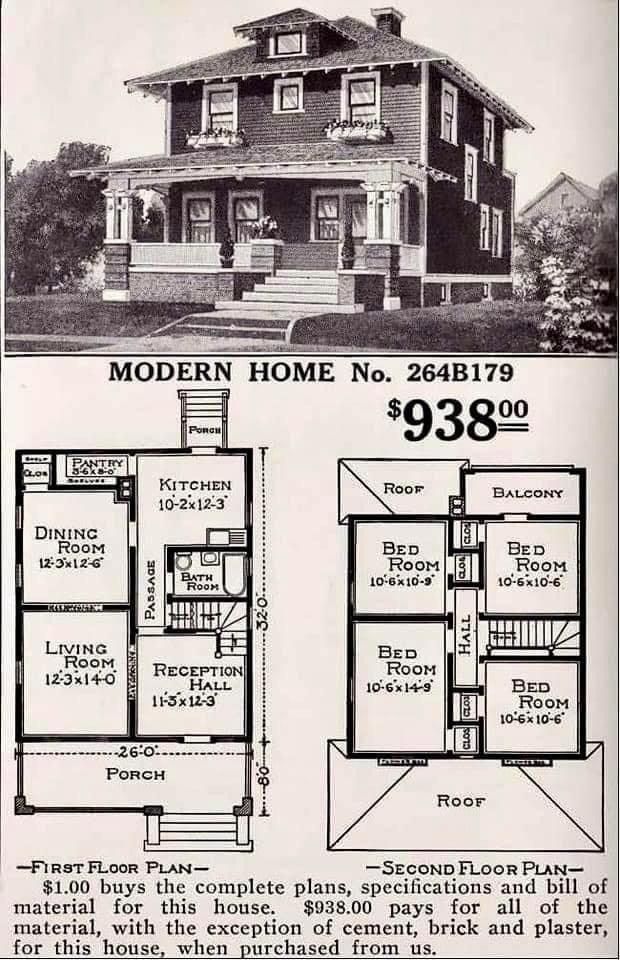
Modular homes may seem like a new trend, but they actually have a long history in American housing. In fact, the concept dates back to the early 20th century when companies like Sears offered prefabricated kit homes. These early homes were a sign of innovation, and today, modular construction is experiencing a resurgence, fueled by the growing need for affordable housing.

So, how does this innovative building method work, and why is it gaining traction now?
How Modular Homes Work: Fast, Efficient, and Cost-Effective

Imagine building a home like assembling a complex puzzle. In modular construction, homes are built off-site in a factory setting, where individual rooms or sections (called “modules”) are constructed with all the necessary framing, utilities, and even interior finishes. Once these modules are complete, they’re transported to the construction site and assembled, much like building blocks coming together to create a fully functional home.
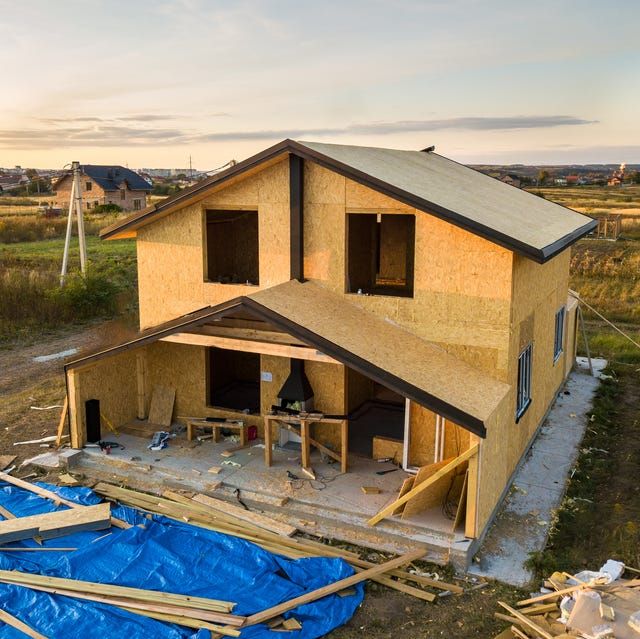

This process has several key advantages over traditional on-site construction, but first, it’s important to clear up a common misconception.
Modular vs. Manufactured Homes: What’s the Difference?

It’s essential to distinguish between modular homes and manufactured homes. While both are prefabricated, modular homes are built to the same local building codes and standards as traditionally constructed homes. They are designed to meet the same safety, durability, and quality requirements as site-built homes, unlike manufactured homes, which follow different construction standards set by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). This means modular homes are just as safe and long-lasting as conventional homes, making them a viable and high-quality option for buyers.
The Benefits of Modular Homes: Why They Could Be the Solution We Need
There are several key advantages to modular construction that make it a compelling solution to the affordable housing crisis:
- Speed: Modular homes can be built in half the time of a traditional home. Because the modules are constructed off-site while the foundation is prepared, the entire process is faster and more efficient.
- Cost: Factory production leads to fewer delays, reduced material waste, and economies of scale, which translates to lower construction costs. These savings can be passed on to homebuyers, making homeownership more affordable.
- Quality: Building in a controlled factory environment ensures consistency in quality. Each module is built with precision and care, reducing the chances of defects and ensuring a durable, high-quality home.
Real-World Impact: Modular Construction in Action

Companies across the U.S. are already proving that modular homes can make a real difference. For example, Vederra Modular in Colorado and Rise Modular in Minnesota are both leading the charge in building affordable, modular housing. These companies are constructing homes at a fraction of the cost of traditional market-rate housing, helping to alleviate some of the pressure on the affordable housing market.
But despite the clear benefits, modular homes still face some hurdles.
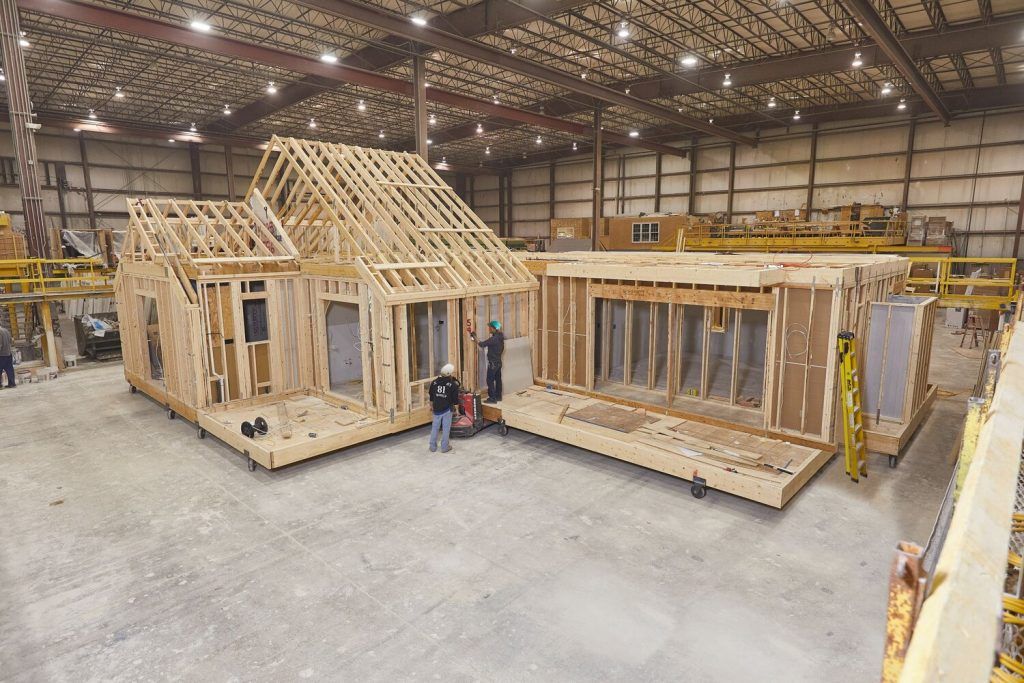

Challenges to Overcome
- Public Perception: Many people still associate modular homes with low quality or inferior construction. Changing this perception will be key to their widespread adoption.
- Financing: Securing financing for modular homes can be difficult because many lenders are unfamiliar with the process. Traditional mortgage providers may be hesitant to fund modular projects, and developers may struggle to secure the capital needed to scale production.
- Scaling Up: In order to meet the growing demand for affordable housing, the modular construction industry will need to expand its production capabilities. Increasing factory output and improving the logistics of delivering these homes to more remote locations will be critical for widespread adoption.
The Future of Housing: Can Modular Homes Lead the Way?

Despite these challenges, the potential of modular construction is undeniable. As the industry gains momentum, it could play a pivotal role in addressing the housing crisis and making homeownership more attainable for more families. With increased awareness, streamlined regulations, and targeted funding, we could see modular homes become a cornerstone of affordable housing development in the years to come.
What are your thoughts on modular homes? Do you think they could help solve the housing affordability crisis? Share your opinions in the comments below—we’d love to hear from you!